RESUMO
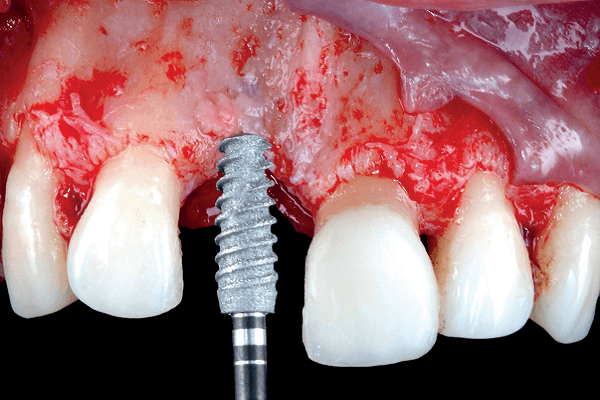
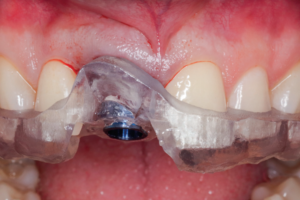
Paciente do sexo feminino, com 28 anos de idade, apresentou-se à clínica odontológica com ausência do incisivo central superior direito. Após avaliação clínica e radiográfica detalhada, menos de 3 mm de espessura óssea remanescente foram detectados. Após a abertura do retalho de espessura total, os procedimentos de osseodensificação foram iniciados. Depois, um implante cônico feito por manufatura aditiva foi instalado, seguido pelo biomaterial ósseo particulado e colocação da membrana absorvível fixada ao cicatrizador, finalizando pela aplicação de um enxerto de tecido conjuntivo subepitelial. Quatro meses depois, uma restauração provisória foi confeccionada e procedimentos cirúrgicos plásticos periodontais foram realizados para nivelamento das margens gengivais. Após dois anos de acompanhamento, os tecidos moles e duros permanecem sem intercorrências.
Palavras-chave – Implantes dentários; Impressão em 3D; Osseodensificação; Regeneração óssea; Zona estética.
ABSTRACT
A female, 28 years-old patient presented to the dental clinics with the lack of the right maxillary central incisor. Upon detailed clinical and radiographic exams, less than 3 mm of bone thickness were detected. After elevation of a full-thickness flap, the osseodensification procedures were initiated. Then, a tapered dental implant made by additive manufacturing was placed, followed by a particulate bone biomaterial and absorbable barrier membrane fixed by the healing abutment, ending the surgery with a subepithelial connective tissue graft. Four months later, a provisional restoration was fabricated and periodontal plastic surgical procedures were made to level the gingival margins. After two years of follow-up, the soft and hard tissues remain free of intercurrences.
Key words – Dental implants; 3D printing; Osseodensification; Bone regeneration; Esthetic zone.
Referências
- Mangano C, Mangano FG, Sammons R. Dental implants from laser fusion of titanium microparticles: from research to clinical applications. J Osseointegration 2009;1(1):9-21.
- Traini T, Mangano C, Sammons RL, Mangano F, Macchi A, Piattelli A. Direct laser metal sintering as a new approach to fabrication of an isoelastic functionally graded material for manufacture of porous titanium dental implants. Dent Mater 2008;24(11):1525-33.
- Hollander DA, Von Walter M, Wirtz T, Sellei R, Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Paar O et al. Structural, mechanical, and in vitro characterization of individually structured Ti-6Al-4V produced by direct laser forming. Biomaterials 2006;27(7):955-63.
- Thieme M, Wieters KP, Bergner F, Scharnweber D, Worch H, Ndop J et al. Titanium powder sintering for preparation of a porous functionally graded material destined for orthopedic implants. J Mater Sci 2001;12(1):225-31.
- Sheela UB, Usha PG, Joseph MM, Melo JS, Thankappan Nair ST, Tripathi A. 3D printing in dental implants. In: 3D printing in medicine and surgery: applications in healthcare. Elsevier, 2020. p.83-104.
- de Carvalho PFM, Clavijo V, da Silva RC, Formiga MC, Joly JC. Instalação e restauração imediata de implante dentário feito por manufatura aditiva e cerâmica bifásica: relato de caso após dois anos de acompanhamento. ImplantNews Reab Oral 2022;7(4):352-9.
- Elsayyad AA, Osman RB. Osseodensification in implant dentistry: a critical review of the literature. Implant Dent 2019;28(3):306-12.
- Huwais S, Meyer E. A novel osseous densification approach in implant osteotomy preparation to increase biomechanical primary stability, bone mineral density, and bone-to-implant contact. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2017;32(1):27-36.
- Trisi P, Berardini M, Falco A, Vulpiani MP. New osseodensification implant site preparation method to increase bone density in low-density bone: in vivo evaluation in sheep. Implant Dent 2016;25(1):24-31.
- Padhye NM, Padhye AM, Bhatavadekar NB. Osseodensification – a systematic review and qualitative analysis of published literature. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 2020;10(1):375-80.
- Inchingolo AD, Inchingolo AM, Bordea IR, Xhajanka E, Romeo DM, Romeo M et al. The effectiveness of osseodensification drilling protocol for implant site osteotomy: a systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis. Materials (Basel) 2021;14(5):1147.
- Frizzera F, Spin-Neto R, Padilha V, Nicchio N, Ghiraldini B, Bezerra F et al. Effect of osseodensification on the increase in ridge thickness and the prevention of buccal peri-implant defects: an in vitro randomized split mouth pilot study. BMC Oral Health 2022;22(1):233.
- Mertens C, Braun S, Krisam J, Hoffmann J. The influence of wound closure on graft stability: an in vitro comparison of different bone grafting techniques for the treatment of one-wall horizontal bone defects. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2019;21(2):284-91.
- Tedesco J, Lee BEJ, Lin AYW, Binkley DM, Delaney KH, Kwiecien JM et al. Osseointegration of a 3d printed stemmed titanium dental implant: a pilot study. Int J Dent 2017;2017:5920714.
- Mangano C, Mangano F, Shibli JA, Luongo G, de Franco M, Briguglio F et al. Prospective clinical evaluation of 201 direct laser metal forming implants: results from a 1-year multicenter study. Lasers Med Sci 2012;27(1):181-9.
- De Angelis P, Manicone PF, Gasparini G, De Angelis S, Liguori MG, De Filippis I et al. Influence of immediate implant placement and provisionalization with or without soft tissue augmentation on hard and soft tissues in the esthetic zone: a one-year retrospective study. Biomed Res Int 2021;2021:8822804.