AUTORES
Amanda Brasil de Freitas
Pós-doutora em Ciências – FMUSP; Monitora na Let’s HOF Academy. Orcid: 0000-0001-5685-9656.
Victor Rogerio
Mestrado em Ciências da Saúde – EPM/Unifesp; Professor na Let’s HOF Academy. Orcid: 0000-0001-7092-5373.
Thiago Gomes Teixeira
Especialista em Harmonização Orofacial – IOA/ITC; Professor na Let’s HOF Academy. Orcid: 0000-0002-9427-6731.
Pietra Roschel de Borba
Especialista em Harmonização Orofacial – IOA/ITC; Professora na Let’s HOF Academy. Orcid: 0000-0002-7330-4502.
Viviane Rabelo
Mestra em Odontologia – USC; Professora na Let’s HOF Academy. Orcid: 0000-0001-5438-7587.
Victor R. M. Lora
Doutor em Prótese Dentária – FOP-Unicamp; Professor na Let’s HOF Academy. Orcid: 0000-0002-1134-8542.
RESUMO
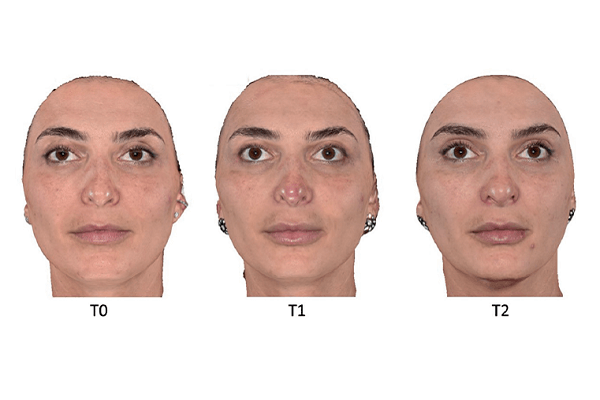
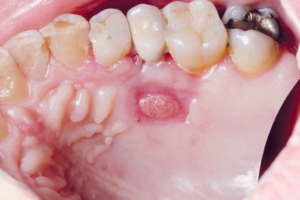
O preenchimento facial com ácido hialurônico tem o nariz como uma das regiões com maior incidência de intercorrências. O eritema na ponta nasal é um sintoma frequente e pode aparecer em diferentes fases após o procedimento. Este estudo relata um caso de preenchimento nasal, com presença de eritema em ponta nasal após 24 horas. Foi realizado o teste de compressão e revascularização, sem sinal de comprometimento vascular. Após o tratamento com anti-inflamatório esteroidal por três dias via oral, houve melhora do quadro. Na literatura, o eritema normalmente regride dentro de quatro semanas, mas também é usualmente tratado com o uso tópico de esteroide de força média, lasers vasculares e luz pulsada. O presente relato apresenta uma abordagem alternativa, não invasiva, acessível e eficaz para redução do tempo de duração do eritema na ponta nasal.
Palavras-chave – Ácido hialurônico; Preenchimento; Nariz; Complicações; Eritema.
ABSTRACT
Facial filling with hyaluronic acid has the nose as one of the regions with the highest incidence of complications. Erythema on the nasal tip is a frequent symptom and can appear at different stages after the procedure. This study reports a case of nasal filling, with the presence of nasal tip erythema after 24 hours. A compression and revascularization test was performed, with no sign of vascular compromise. After treatment with a orally steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for 3 days, the condition improved. In the literature, erythema usually resolves within 4 weeks, but it is also usually treated with topical medium-strength steroids, vascular lasers, and pulsed light. Our report presents an alternative, non-invasive, accessible and effective approach to reduce the duration of nasal tip erythema.
Key words – Hyaluronic acid; Filler; Nose; Complications; Erythema.
Referências
- Kim JH, Ahn DK, Jeong HS, Suh IS. Treatment algorithm of complications after filler injection: based on wound healing process. J Korean Med Sci 2014;29(3):S176-82.
- Funt D, Pavicic T. Dermal fillers in aesthetics: an overview of adverse events and treatment approaches. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2013;6:295-316.
- Xiong M, Chen C, Sereda Y, Garibyan L, Avram M, Lee KC. Retrospective analysis of the MAUDE database on dermal filler complications from 2014-2020. J Am Acad Dermatol 2022;87(5):1158-60.
- Oranges CM, Brucato D, Schaefer DJ, Kalbermatten DF, Harder Y. Complications of nonpermanent facial fillers: a systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2021;9(10):e3851.
- Singh P, Vijayan R, Nikkhah D. Filler rhinoplasty: evidence, outcomes, and complications. Aesthet Surg J 2018;38(11):NP165-NP7.
- Segreto F, Marangi GF, Cerbone V, Alessandri-Bonetti M, Caldaria E, Persichetti P. Nonsurgical rhinoplasty: a graft-based technique. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2019;7(6):e2241.
- Kumar V, Jain A, Atre S, Shome D, Kapoor R, Doshi K et al. Non-surgical rhinoplasty using hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: a systematic review. J Cosmet Dermatol 2021;20(8):2414-24.
- Liew S, Scamp T, de Maio M, Halstead M, Johnston N, Silberberg M et al. Efficacy and safety of a hyaluronic acid filler to correct aesthetically detracting or deficient features of the Asian nose: a prospective, open-label, long-term study. Aesthet Surg J 2016;36(7):760-72.
- Arron ST, Neuhaus IM. Persistent delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to injectable non-animal-stabilized hyaluronic acid. J Cosmet Dermatol 2007;6(3):167-71.
- Urdiales-Gálvez F, Delgado NE, Figueiredo V, Lajo-Plaza JV, Mira M, Moreno A et al. Treatment of soft tissue filler complications: expert consensus recommendations. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2018;42(2):498-510.
- Marwa K, Kondamudi NP. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction [On-line]. Disponível em <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562228/>. Acesso em: 22-8-2022.
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek A, Zdanowska N, Wygonowska E, Placek W. The immunogenicity of hyaluronic fillers and its consequences. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2021;14:921-34.
- Murat E, Conrozier T. Impact of the skin disinfection with quaternary ammonium salts on the rheological properties of hyaluronic acid viscosupplements. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 2021;35(4):27832-5.
- Cohen JL, Bhatia AC. The role of topical vitamin K oxide gel in the resolution of postprocedural purpura. J Drugs Dermatol 2009;8(11):1020-24.
- Brys AK, Cox SE. Early-onset sweet-like dermatitis after facial hyaluronic acid filler injection. Dermatol Surg 2020;46(12):1759-61.
- Ozturk CN, Li Y, Tung R, Parker L, Piliang MP, Zins JE. Complications following injection of soft-tissue fillers. Aesthet Surg J 2013;33(6):862-77.
- Signorini M, Liew S, Sundaram H, De Boulle KL, Goodman GJ, Monheit G et al. Global aesthetics consensus: avoidance and management of complications from hyaluronic acid fillers-evidence- and opinion-based review and consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg 2016;137(6):961e-71e.
- Coimbra DD, de Oliveira BS, Uribe NC. Preenchimento nasal com novo ácido hialurônico: série de 280 casos. Surg Cosmet Dermatology 2015;7(4):320-6.
- Johnson ON, Kontis TC. Nonsurgical rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 2016;32(5):500-6.