RESUMO
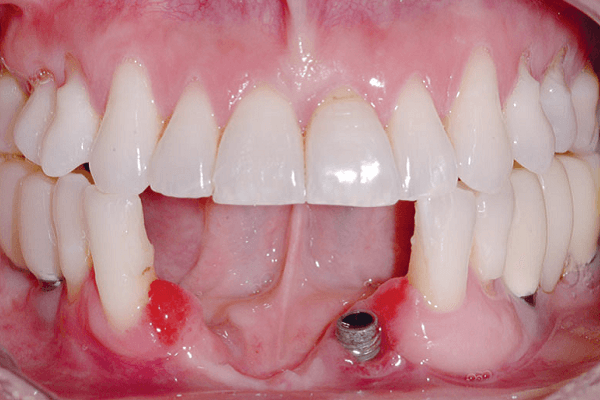
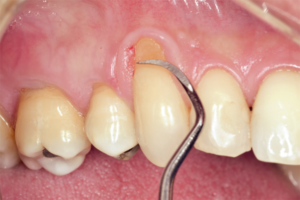
A reabsorção do rebordo ósseo alveolar desdentado ocorre no sentido horizontal e vertical, e, dependendo da região, pode dificultar ou inviabilizar a reabilitação com implantes osseointegrados. O objetivo deste relato foi apresentar uma alternativa de tratamento em regiões de atrofia óssea vertical, utilizando a técnica de osteotomia sanduíche associada ao enxerto ósseo xenógeno na região anterior da mandíbula e posterior reabilitação com implantes osseointegrados. Paciente do sexo feminino, com 38 anos de idade, leucoderma, sistemicamente saudável e apresentando boa higiene oral, compareceu à clínica odontológica queixando-se de estética e função mastigatória prejudicadas. Ao exame clínico e imaginológico, foi observado um extenso defeito ósseo vertical na região anterior de mandíbula, uma pequena faixa de mucosa ceratinizada, presença de um implante na região do 32 com quatro roscas expostas e tecido peri-implantar inflamado. O plano de tratamento elaborado foi: remoção do implante; reconstrução óssea da região anterior de mandíbula por meio da técnica de osteotomia sanduíche; reabertura da área enxertada e instalação dos implantes; reabertura dos implantes associada ao enxerto gengival livre; e instalação dos munhões universais para confecção dos provisórios. O controle clínico e radiográfico após um ano da instalação das coroas provisórias revelou manutenção dos resultados obtidos e satisfação por parte da paciente e do cirurgião-dentista. Concluiu-se que a técnica de osteotomia sanduíche associada ao enxerto ósseo xenógeno para reconstrução de região com intensa atrofia óssea vertical mostrou-se viável e previsível para aumento em altura da região anterior da mandíbula e posterior reabilitação com implantes osseointegrados, restabelecendo estética e função.
Palavras-chave – Aumento do rebordo alveolar; Implantes dentários; Perda do osso alveolar; Procedimentos cirúrgicos reconstrutivos.
ABSTRACT
Reabsorption of the edentulous alveolar bone marrow occurs horizontally and vertically, and depending on the region, it may hamper or prevent implant rehabilitation. The aim of this report is to present an alternative treatment for regions of vertical bone atrophy using the sandwich osteotomy technique associated with the xenogenous bone graft in the anterior region of the mandible and posterior implant rehabilitation. A 38 years-old, female patient, systemically healthy, with good oral hygiene attended the dental clinic complaining of impaired aesthetic and masticatory function. The clinical and imaging examination revealed an extensive vertical bone defect in the anterior region of the mandible, a small range of keratinized mucosa, presence of an implant in the region of 32 with 4 exposed threads and inflamed peri implant tissue. The treatment plan was elaborated: implant removal; bone reconstruction of the anterior mandible region using the sandwich osteotomy technique; reopening of the grafted area and implant installation; reopening of the implants associated with the free gingival graft and installation of the prosthetic component and preparation of the provisional ones. The clinical and radiographic control after 1 year of installation of the provisional crowns revealed maintenance of the obtained results and satisfaction on the part of the patient and the dental surgeon. It was concluded that the sandwich osteotomy technique for the reconstruction of the region with intense vertical bone atrophy proved to be viable and predictable for height increase of the anterior region of the mandible and posterior implant rehabilitation restoring aesthetics and function.
Key words – Alveolar ridge augmentation; Dental implants; Alveolar bone loss; Reconstructive surgical procedures.
Referências
- Choi BH, Lee SH, Huh JY, Han SG. Use of the sandwich osteotomy plus an interpositional allograft for vertical augmentation of the alveolar ridge. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2004;32(1):51-4.
- Tanaka K, Sailer I, Kataoka Y, Nogami S, Takahashi T. Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of the posterior maxillary region: a case report with 9-year follow-up. Int J Implant Dent 2017;3(1):20.
- Noia CF, Ortega-Lopes R, Kluppel LE, Sa BC. Sandwich osteotomies to treat vertical defects of the alveolar ridge. Implant Dent 2017;26(1):101-5.
- Bormann KH, Suarez-Cunqueiro MM, von See C, Tavassol F, Dissmann JP, Ruecker M et al. Forty sandwich osteotomies in atrophic mandibles: a retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2011;69(6):1562-70.
- Bell RE. Palatal approach to the anterior maxillary sandwich osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2013;71(6):1005-9.
- Moon JW, Choi BJ, Lee WH, An KM, Sohn DS. Reconstruction of atrophic anterior mandible using piezoelectric sandwich osteotomy: a case report. Implant Dent 2009;18(3):195-202.
- Simion M, Jovanovic SA, Tinti C, Benfenati SP. Long-term evaluation of osseointegrated implants inserted at the time or after vertical ridge augmentation: a retrospective study on 123 implants with 1-5 year follow up. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12(1):35-45.
- Herford AS, Tandon R, Stevens TW, Stoffella E, Cicciu M. Immediate distraction osteogenesis: the sandwich technique in combination with rhBMP-2 for anterior maxillary and mandibular defects. J Craniofac Surg 2013;24(4):1383-7.
- Chiapasco M, Romeo E, Casentini P, Rimondini L. Alveolar distraction osteogenesis for the correction of vertically deficient edentulous ridges: a multicenter prospective study on humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004;19(3):399-407.
- Hasbemi H, Javidi B. Comparison between interpositional bone grafting and osteogenic alveolar distraction in alveolar bone reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010;68(8):1853-8.
- Herford AS. Distraction osteogenesis: a surgical option for restoring missing tissue in the anterior esthetic zone. J Calif Dent Assoc 2005;33(11):889-95.
- Chiapasco M, Zaniboni M, Rimondini L. Autogenous onlay bone grafts vs. alveolar distraction osteogenesis for the correction of vertically deficient edentulous ridges: a 2–4-year prospective study on humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007;18(4):432-40.
- Thoma DS, Zeltner M, Hüsler J, Hämmerle CH, Jung RE. EAO Supplement Working Group 4 – EAO CC. Short implants versus sinus lifting with longer implants to restore the posterior maxilla: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2015;26(suppl.11):154-69.
- Schettler D. Sandwich technique with cartilage transplant for raising the alveolar process in the lower jaw. Fortschr Kiefer Gesichtschir 1976;20:61-3.
- Schettler D, Holtermann W. Clinical and experimental results of a sandwich technique for mandibular alveolar ridge augmentation. J Maxillofac Surg 1977;5(3):199-202.
- Stellingsma C, Raghoebar GM, Meijer HJA, Batenburg RHK. Reconstruction of the extremely resorbed mandible with interposed bone grafts and placement of endosseous implants. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1998;36(4):290-5.
- Stoelinga PJ, Tideman H, Berger JS, de Koomen HA. Interpositional bone graft augmentation of the atrophic mandible: a preliminary report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1978;36(1):30-2.
- Misch CE. Implantes dentais contemporâneos (3a ). Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier Brasil, 2011.
- Rachmiel A, Emodi O, Rachmiel D, Israel Y, Shilo D. Sandwich osteotomy for the reconstruction of deficient alveolar bone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2018;47(10):1350-7.
- Bagheri SC. Revisão clínica de cirurgia bucomaxilofacial (2a). Rio de Janeiro: Editora Elsevier, 2015.
- Mehta KS, Prasad K, Shetty V, Ranganath K, Lalitha R, Dexith J et al. Effect of alveolar segmental sandwich osteotomy on alveolar height: a preliminary study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2017;16(4):471-8.
- Felice P, Pistilli R, Lizio G, Pellegrino G, Nisii A, Marchetti C. Inlay versus onlay iliac bone grafting in atrophic posterior mandible: a prospective controlled clinical trial for the comparison of two techniques. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2009;11(suppl.1):69-82.
- Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg 1980;38(8):613-6.
- Wood RM, Moore DL. Grafting of the maxillary sinus with intraorally harvested autogenous bone prior to implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1988;3(3):209-14.
- Kalk WW, Raqhoebar GM, Jansma J, Boering G. Morbidity from iliac crest bone harvesting. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54(12):1424-9 (discussion 1430).
- Koerdt S, Ristow O, Wannhoff A, Kübler AC, Reuther T. Expression of growth factors during the healing process of alveolar ridge augmentation procedures using autogenous bone grafts in combination with GTR and an anorganic bovine bone substitute: an immunohistochemical study in the sheep. Clin Oral Investig 2014;18(1):179-88.
- Triplett RG, Schow SR. Autologous bone grafts and endosseous implants: complementary techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54(4):486-94.