RESUMO
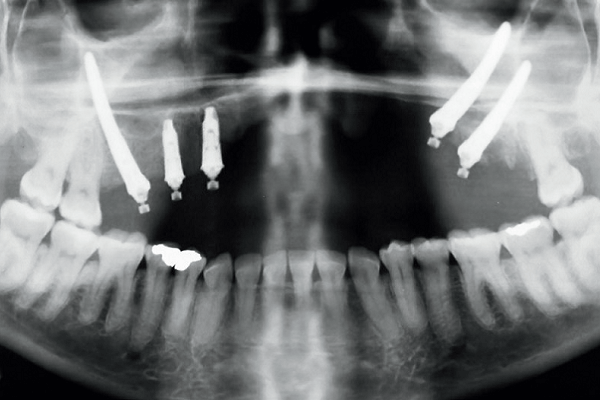
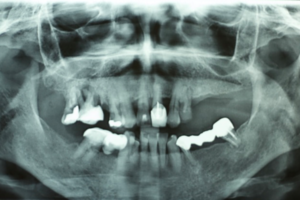
O ameloblastoma é um tumor odontogênico benigno, localmente invasivo, capaz de infiltrar-se pelos espaços medulares do osso e, quando em estágio inicial, geralmente não apresenta indícios radiográficos ou macroscópicos. Muitas vezes, pacientes submetidos a tratamento ressectivo perdem grande parte da maxila ou mandíbula, necessitando de uma alternativa de tratamento para restabelecer a função e a estética. O objetivo deste relato de caso foi apresentar um acompanhamento de quatro anos de uma reabilitação com implantes zigomáticos em paciente submetido à ressecção de maxila anterior devido a um tumor odontogênico do tipo ameloblastoma. Quatro meses após a realização da cirurgia de ressecção do ameloblastoma na região anterior de maxila, foram instalados dois implantes com ancoragem zigomática no lado esquerdo, um implante com ancoragem zigomática no lado direito e dois implantes regulares hexágono externo no lado direito. Em seguida, foi feita uma prótese provisória imediata. Seis meses depois, os implantes foram carregados com a prótese final em resina acrílica. Após quatro anos de acompanhamento, não foram observados sintomas dolorosos, inflamação ou infecção peri-implantar, instabilidade do implante ou reabsorção óssea. No presente caso, a reabilitação da maxila atrófica com implantes no osso zigomático proporcionou bons resultados funcionais e estéticos a longo prazo. Assim, o uso de implantes zigomáticos associados a implantes padrão oferece vantagens na reabilitação de maxilares severamente reabsorvidos, principalmente quando a indicação é feita corretamente e com o conhecimento da técnica cirúrgica.
Palavras-chave – Ameloblastoma; Tumores odontogênicos; Implantes dentários.
ABSTRACT
Ameloblastoma is a benign, locally invasive odontogenic tumor capable of infiltrating the bone marrow spaces, and when at the initial stage, it generally does not show radiographic or macroscopic evidence. Patients undergoing resection treatment lose a large part of the maxilla or mandible, requiring an alternative treatment to re-establish the function and aesthetics. The objective of this case report was to present a 4-years follow-up of a rehabilitation with zygomatic implants in a patient submitted to anterior maxillary resection due to an odontogenic tumor of the ameloblastoma type. After 4 months of the ameloblastoma resection surgery in the anterior maxillary region, 2 implants were placed with zygomatic anchoring on the left side, 1 implant with zygomatic anchoring on the right side and 2 regular external hexagon implants placed on the right side and then it was done an immediate provisional prosthesis. Six months later, the implants were loaded with the final acrylic resin prosthesis. After 4-years of follow-up no painful symptoms, inflammation or peri-implant infection, implant instability or bone resorption were observed. In the present case, the atrophic maxilla rehabilitation with implants in the zygomatic bone provided long-term functional and aesthetic results. Thus, the zygomatic implants associated with standard implants offers advantages in severely reabsorbed maxillae rehabilitation, especially when the indication is made correctly and also with the knowledge of the surgical technique.
Key words – Ameloblastoma; Odontogenic tumors; Dental implants.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.