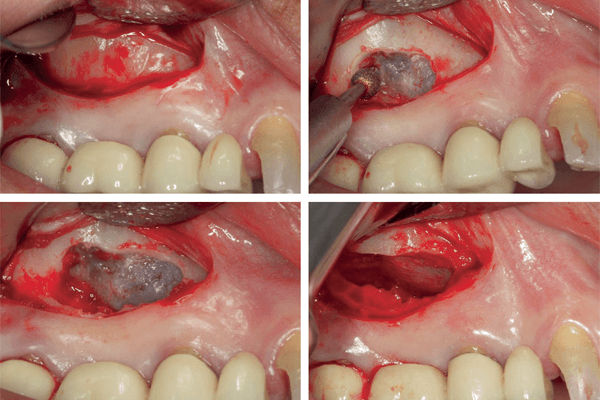
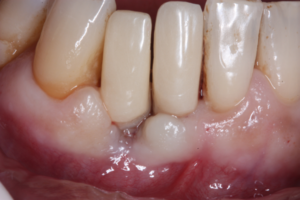
Artigo científico descreve uma nova e conservadora técnica de enxertia sinusal acima das raízes de dentes condenados.
AUTORES
Ricardo Kleiner Ciantelli
Mestre e doutor em Implantodontia – São Leopoldo Mandic; Coordenador da especialização em Implantodontia – ABO Sorocaba.
Orcid: 0000-0001-7124-6495.
Thales Lippi Ciantelli
Mestre em Ortodontia – USP; Professor de especialização em Ortodontia – CPO Sorocaba.
Orcid: 0000-0003-3828-235X.
Letícia Florindo Pereira
Mestranda em Reabilitação Oral (Depto. de Prótese e Periodontia) – USP.
Orcid: 0000-0001-9200-9827.
Erton Massamitsu Miyasawa
Especialista e mestre em Implantodontia, professor assistente dos cursos de especialização e atualização em Implantodontia – ABO Sorocaba.
Orcid: 0000-0001-9770-4853.
Vinicius Ferreira Bizelli
Doutorando (Depto. de Diagnóstico e Cirurgia) – Unesp Araçatuba; Professor de especialização em Implantes – Tokape/ITI Study Club Director.
Orcid: 0000-0003-1813-3509.
Paulo Sérgio Perri de Carvalho
Professor (Depto. de Estomatologia e Biologia Oral) – FOB-USP; Membro do Depto. de Implantodontia – Centro de Pesquisa São Leopoldo Mandic.
Orcid: 0000-0003-1775-3108.
RESUMO
O objetivo desse relato de caso foi descrever uma nova e conservadora técnica de enxertia sinusal acima das raízes de dentes condenados, mantendo-os na cavidade oral até a remodelação do enxerto ósseo, permitindo, possivelmente, a aplicação da carga imediata. Paciente do sexo feminino com 57 anos de idade, leucoderma, sistemicamente saudável, procurou atendimento especializado com queixa principal de dor e insatisfação com a prótese. Ao exame clínico e radiográfico, observou-se a presença de uma prótese parcial fixa (PPF) do elemento 14 até 17, sendo que os pilares 15 e 17 estavam condenados e o 14 era um cantiléver. O tratamento proposto foi o levantamento de seio maxilar com enxerto ósseo xenógeno particulado (1-2 mm) e auxílio dos agregados plaquetários (I-PRF e L-PRF) previamente à exodontia dos pilares da PPF. Com seis meses de pós-operatório, uma radiografia panorâmica foi solicitada e três implantes de conexão interna foram instalados – 4,3 x 10 mm (posição 14) e 4,3 x 11,5 mm (posições 15 e 16). A reabertura dos implantes foi realizada com 21 dias de pós-operatório, e as coroas provisórias foram confeccionadas para o condicionamento gengival. Após o condicionamento, as próteses sobre implantes definitivas foram instaladas e a paciente atualmente está em acompanhamento clínico há um ano. Apesar das limitações, concluiu-se que a técnica de enxertia sinusal previamente à exodontia de dentes condenados pode ser uma técnica viável e previsível, proporcionando maior conforto ao paciente e menor morbidade.
Palavras-chave – Seio maxilar; Biomateriais; Implantes dentários; I-PRF; L-PRF.
ABSTRACT
The objective of this case report was to describe a new and conservative technique for sinus grafting above the roots of hopless teeth, keeping them in the oral cavity until the bone graft remodels, possibly allowing the application of immediate loading. A 57-year-old female patient, caucasian, systemically healthy, sought specialized care with a chief complaint of pain and dissatisfaction with the prosthesis. The clinical and radiographic examination revealed the presence of a fixed partial denture (FPD) from elements #14 to #17, with hopless dental abutments at #15 and #17 condemned and the pillar #14 as the cantilever. The proposed treatment was the lifting of the maxillary sinus with a xenogeneic particulate bone graft (1-2 mm) and the aid of platelet aggregates (I-PRF and L-PRF) before the extraction of the FPD abutments. After 6 months postoperatively, a panoramic radiograph was requested and three internal connection dental implants 4.3 x 10 mm (position 14) and 4.3 x 11.5 mm (positions 15 and 16) were installed. The dental implants were exposed 21 days after surgery and the provisional crowns made for gingival conditioning. After gingival conditioning, the definitive implant prosthesis was installed and the patient is currently under the first year of follow-up. Despite the limitations, we concluded that the technique of sinus grafting, before the extraction of condemned teeth, can be viable and predictable, providing greater comfort to the patient and less morbidity
Key words – Maxillary sinus; Biomaterials; Dental implants; I-PRF; L-PRF
Referências
- Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2003;23(4):313-23.
- Mecall RA, Rosenfeld AL. Influence of residual ridge resorption patterns on implant fixture placement and tooth position.1. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1991;11(1):8-23.
- Cawood JI, Howell RA. A classification of the edentulous jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1988;17(4):232-6.
- Sanz M, Donos N, Alcoforado G, Balmer M, Gurzawska K, Mardas N et al. Therapeutic concepts and methods for improving dental implant outcomes. Summary and consensus statements. The 4th EAO Consensus Conference 2015. Clin Oral Implants Res 2015;26(suppl.11):202-6.
- Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg 1980;38(8):613-6.
- Tatum H. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstruction. Dent Clin North Am 1986;30(2):207-29.
- Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R et al. Effectiveness of sinus lift procedures for dental implant rehabilitation: a Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol 2010;3(1):7-26.
- Lozada JL, Caplanis N, Proussaefs P, Willardsen J, Kammeyer G. Platelet-rich plasma application in sinus graft surgery: part I – background and processing techniques. J Oral Implantol 2001;27(1):38-42.
- Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJJ, Mouhyi J et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006;101(3):37-44.
- Silva FB, Dutra KM, Albuquerque AFM, Fiamengui Filho JF. Evidências científicas do uso da fibrina rica em plaquetas em odontologia: uma revisão integrativa. ImplantNewsPerio 2017;2(1):57-63.
- de Almeida FMR, dos Santos DCL, Fuziama CDH, Nunziata DF, dos Santos RA. Uso da fibrina rica em plaquetas na Implantodontia. ImplantNewsPerio 2017;2(2):271-80.
- Marx RE, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt RM, Schimmele SR, Strauss JE, Georgeff KR. Platelet-rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1998;85(6):638-46.
- de Obarrio JJ, Araúz-Dutari JI, Chamberlain TM, Croston A. The use of autologous growth factors in periodontal surgical therapy: platelet gel biotechnology – case reports. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2000;20(5):486-97.
- Zhou X, Hu XL, Li JH, Lin Y. Minimally invasive crestal sinus lift technique and simultaneous implant placement. Clin J Dent Res 2017;20(4):211-8.
- Stern A, Green J. Sinus lift procedures: an overview of current techniques. Dent Clin North Am 2012;56(1):219-33.
- Vieira FLD, Orem IB, Minozzo C, Lavinas FPS, de Oliveira Jr. NG, Elias WC. Utilização de fibrina leucoplaquetária autóloga na recuperação de perfuração crítica da membrana sinusal. ImplantNewsPerio 2016;1(7):1293-9.
- Pessoa Neto JV, Sabóia MAV, Albuquerque AFM, da Silva BR. Atividade antimicrobiana da fibrina rica em plaquetas frente a cepas bacterianas orais. ImplantNewsPerio 2018;3(4):655-61.
- da Costa ALCC, Ramos Neto AS, das Neves DM, Silva FGO, Simão GML. Levantamento de seio maxilar com instalação simultânea de implante utilizando fibrina rica em plaquetas e leucócitos como único biomaterial: avaliação tomográfica do ganho ósseo após seis meses. ImplantNews 2014;11(2):213-22.
- Bornstein MM, Wittneben JG, Brägger U, Buser D. Early loading at 21 days of non-submerged titanium implants with a chemically modified sandblasted and acid-etched surface: 3-year results of a prospective study in the posterior mandible. J Periodontol 2010;81(6):809-18.
- Makowiecki A, Hadzik J, Błaszczyszyn A, Gedrange T, Dominiak M. An evaluation of superhydrophilic surfaces of dental implants – a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2019;19(1):79.
- Ferreira PHSG, Bizelli VF, Bittencourt Junior D, Fontão FGK, Bassi APF. Tomographic and histological study of maxillary sinus lift technique and dental implants placement without use of biomaterial with a 36-month follow-up: case report. Research, Society and Development 2021;10(2):e31810212558.
- Vazquez JCM, de Rivera ASG, Gil HS, Mifsut RS. Complication rate in 200 consecutive sinus lift procedures: guidelines for prevention and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2014;72(5):892-901.
- Mourão CFAB, de Mello-Machado RC, Javid K, Moraschini V. The use of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin in the management of soft tissue healing and pain in post-extraction sockets: a randomized clinical trial. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2020;48(4):452-7.
- Pitzurra L, Jansen IDC, de Vries TJ, Hoogenkamp MA, Loos BG. Effects of L-PRF and A-PRF+ on periodontal fibroblasts in in vitro wound healing experiments. J Periodontal Res 2020;55(2):287-95.
- Fareen HF, Ashok V, Rengalakshmi S, Subhashree R. Dental implants in maxillary anteriors for young adults: a retrospective study. J Long Term Eff Med Implants 2021;31(4):27-31.
- Fonteyne E, De Bruyn H, De Fruyt F. Quality of life and social participation in dental rehabilitation: a personality and multi-informant perspective. J Dent 2020;103S:100021.
- Markovic A, Mišić T, Janjić B et al. Immediate vs. early loading of bone level tapered dental implants with hydrophilic surface in fully edentulous maxilla: clinical and patient-centered outcomes. J Oral Implantol 2022;48(5):359-69.
- Neves FD, Silveira-Júnior CD, Coró V, Silva-Neto JP, Simamoto-Júnior PC, Prado CJ. Gingival conditioning in an implant-supported prosthesis: a clinical report. J Oral Implantol 2013;39(4):483-5.
- Skirbutis G, Dzingutė A, Masiliūnaitė V, Šulcaitė G, Žilinskas J. PEEK polymer’s properties and its use in prosthodontics. A review. Stomatologija 2018;20(2):54-8.
- Gonçalves GSY, de Magalhães KMF, Rocha EP, dos Santos PH, Assunção WG. Oral health-related quality of life and satisfaction in edentulous patients rehabilitated with implant-supported full dentures all-on-four concept: a systematic review. Clin Oral Investig 2022;26(1):83-94.