RESUMO
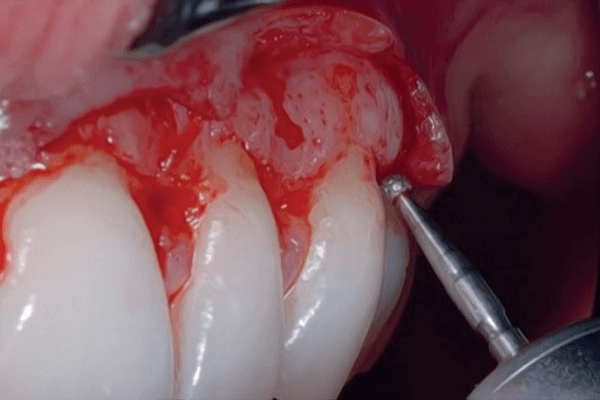
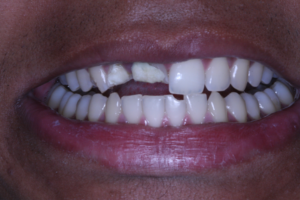
O sorriso gengival pode ser causado por vários fatores e é considerado desarmônico, trazendo desconforto ao paciente. Essa condição pode ser corrigida com procedimentos periodontais associados ou não a procedimentos restauradores. Porém, as técnicas disponíveis atualmente para se trabalhar em áreas estéticas ainda são pouco discutidas. Dessa forma, este artigo teve como objetivo trazer o planejamento e a resolução de três casos clínicos de sorriso gengival, nos quais as pacientes necessitavam de cirurgia de aumento de coroa em região anterior de maxila para correção de sorriso gengival e alinhamento das margens gengivais. Entretanto, uma vez que cada paciente apresentava características distintas e únicas, a escolha e a execução da técnica cirúrgica foram diferentes em cada caso clínico, sendo discutidos e comparados os benefícios e riscos de cada uma das técnicas escolhidas. O caso 1 foi realizado com uma gengivectomia de bisel interno marginal e utilizando a técnica de scrapping gengival. No caso 2 foi realizada gengivectomia de bisel interno marginal utilizando uma técnica de osteotomia flapless. No caso 3, realizou-se gengivectomia de bisel interno marginal com retalho de espessura total, com preservação de papila e ostectomia/ osteoplastia. Ao considerar os casos demonstrados, pôde-se concluir que existem várias possiblidades terapêuticas para correção do sorriso gengival, que devem ser determinadas pelo conhecimento do operador após um completo e minucioso exame clínico e de imagem, levando em consideração a anatomia das estruturas que compõem o sorriso do paciente, visando obter o sucesso clínico com um melhor pós-operatório.
Palavras-chave – Sorriso gengival; Aumento de coroa estético; Cirurgia plástica periodontal.
ABSTRACT
The gingival smile can be caused by several factors and promotes a disharmonious smile, bringing discomfort to the patient. This condition can be corrected by periodontal procedures associated or not with restorative procedures. However, the techniques currently available for working in aesthetic areas are still little discussed. Thus, this article aims to bring the planning and resolution of three clinical cases of gingival smile, where all three patients needed crown lengthening surgery in the anterior region of the maxilla to correct gingival smile and balancing the gingival margins. However, since each patient had distinct and unique characteristics, the choice and execution of the surgical technique were different in each clinical case, and the benefits and risks of each of the chosen techniques were discussed and compared. Case 1 was performed with a marginal internal bevel gingivectomy and using a gingival scraping technique. Case 2, marginal internal bevel gingivectomy was performed using an ostectomy technique without a flap. Case 3, marginal internal bevel gingivectomy, with full thickness flap with preservation of the papilla and ostectomy/osteoplasty. When considering the demonstrated cases, it can be verified that there are several therapeutic possibilities to correct the gingival smile, which must be determined by the operator’s knowledge, after complete and thorough clinical and image examination, considering the anatomy of the structures that compose the patient’s smile, aiming clinical success with the patient’s best postoperative results.
Key words – Gingival smile; Cosmetic crown lengthening; Periodontal plastic surgery.
Referências
- Lanning SK, Waldrop TC, Gunsolley JC, Maynard JG. Surgical crown lengthening: evaluation of the biological width. J Periodontol 2003;74(4):468-74.
- Marzadori M, Stefanini M, Sangiorgi M, Mounssif I, Monaco C, Zucchelli G. Crown lengthening and restorative procedures in the esthetic zone. Periodontol 2000 2018;77(1):84-92.
- Işiksal E, Hazar S, Akyalçin S. Smile esthetics: perception and comparison of treated and untreated smiles. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2006;129(1):8-16.
- Dolt AH 3rd, Robbins JW. Altered passive eruption: an etiology of short clinical crowns. Quintessence Int 1997;28(6):363-72.
- Wagenberg BD. Surgical tooth lengthening: biologic variables and esthetic concerns. J Esthet Dent 1998;10(1):30-6.
- Mondelli J. Estética e cosmética em clínica integrada restauradora. São Paulo: Quintessense, 2006. p.281.
- Deas DE, Moritz AJ, McDonnell HT, Powell CA, Mealey BL. Osseous surgery for crown lengthening: a 6-month clinical study. J Periodontol 2004;75(9):1288-94.
- Brägger U, Lauchenauer D, Lang NP. Surgical lengthening of the clinical crown. J Clin Periodontol 1992;19(1):58-63.
- Roshna T, Nandakumar K. Anterior esthetic gingival depigmentation and crown lengthening: report of a case. J Contemp Dent Pract 2005;6(3):139-47.
- Garber DA, Salama MA. The aesthetic smile: diagnosis and treatment. Periodontol 2000 1996;11:18-28.
- Malkinson S, Waldrop TC, Gunsolley JC, Lanning SK, Sabatini R. The effect of esthetic crown lengthening on perceptions of a patient’s attractiveness, friendliness, trustworthiness, intelligence, and self-confidence. J Periodontol 2013;84(8):1126-33.
- Arnett GW, Bergman RT. Facial keys to orthodontic diagnosis and treatment planning. Part I. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1993;103(4):299-312.
- Ribeiro FV, Hirata DY, Reis AF, Santos VR, Miranda TS, Faveri M et al. Open-flap versus flapless esthetic crown lengthening: 12-month clinical outcomes of a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 2014;85(4):536-44.