RESUMO
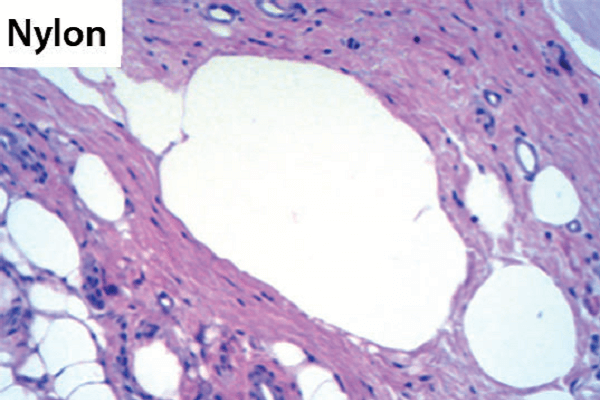
Objetivo: avaliar microscopicamente a reação tecidual aos fios de sutura utilizados no plano muscular de ratos. Material e métodos: foram utilizados 18 ratos da espécie Rattus/Norvegicus (linhagem Albinus/Wistar), divididos em três grupos de seis animais cada. Foram realizadas suturas no tecido muscular com fios de seda, nylon, polipropileno e poliglactina 910, sendo os grupos divididos de acordo com o tempo de eutanásia. Grupo 1: os animais receberam suturas com fio de seda, nylon, polipropileno e poliglactina 910 (n=6), e foram eutanasiados cinco dias após o ato operatório; os animais dos grupos 2 e 3 receberam as mesmas suturas e foram eutanasiados dez e 20 dias após o procedimento cirúrgico. Resultados: nos períodos analisados, houve reação inflamatória intensa ao redor do fio de seda; reação inflamatória moderada aos cinco dias no fio de poliglactina 910, decrescente no período de dez dias e ausente aos 20 dias; e ausência de reação inflamatória nos fios de nylon e polipropileno. Conclusão: as reações inflamatórias diferiram em todos os fios estudados, sendo mais intensas quando o fio de seda foi utilizado. O fio de poliglactina 910 apresentou uma reação inflamatória decrescente nos períodos estudados, portanto foi observado um alto grau de biocompatibilidade nos fios de nylon e polipropileno.
Palavras-chave – Suturas; Ratos Wistar; Materiais biocompatíveis.
ABSTRACT
Objective: to evaluate microscopically the tissue reaction to different thread sutures used in the muscular plane of rats. Material and methods: 18 rats of the species Rattus Norvegicus (Albinus/Wistar) were divided into 3 groups of 6 animals each. Sutures were made in the muscle tissue with silk, nylon, polypropylene, and polyglactin 910 threads, and the groups were divided according to the time of euthanasia. Group 1: the animals received sutures with threaded silk, nylon, polypropylene, and polyglactin 910 (n=6) and were euthanized 5 days after the surgery; the animals in groups 2 and 3 received the same sutures and were euthanized 10 and 20 days after the surgical procedure. Results: an intense infl ammatory reaction was found around the silk thread, with moderate inflammatory reaction at 5 days in polyglactin 910, which reduced in 10 days and became absent at 20 days; also, the absence of an inflammatory reaction in nylon and polypropylene threads was identified. Conclusion: the inflammatory reactions differed in all the studied threads, being more intense when the silk thread was used; the polyglactin 910 thread showed a decreasing inflammatory reaction in the studied periods. A high degree of biocompatibility was observed in nylon and polypropylene threads.
Key words – Sutures; Wistar rats; Biocompatible materials.
Referências
- Santos JS, Kemp R. Fundamentos básicos para a cirurgia e cuidados perioperatórios. Medicina (Ribeirão Preto. Online) 2011;44(1):2.
- Burkhardt R, Lang NP. Influence of suturing on wound healing. Periodontol 2000 2015;68(1):270-81.
- Ribeiro CMB, Silva Júnior VA, Silva Neto JC, Vasconcelos BCE. Estudo clínico e histopatológico da reação tecidual às suturas interna e externa dos fios monofilamentares de nylon e poliglecaprone 25 em ratos. Acta Cir Bras 2005;20(4):284-91.
- Barros M, Gorgal R, Machado AP, Correia A, Montenegro N. Acta Med Port 2011;24(suppl.4):1051-6.
- Yaltirik M, Dedeoglu K, Bilgic B, Koray M, Ersev H, Issever H et al. Comparison of four different suture materials in soft tissues of rats. Oral Dis 2003;9(6):284-86.
- Vats U, Pandit Suchitra N. Comparison of efficacy of three suture materials, i.e., poliglecaprone 25, polyglactin 910, polyamide, as subcuticular skin stitches in post-cesarean women: a randomized clinical trial. J Obstet Gynaecol India 2014;64(1):14-8.
- Nary Filho H, Matsumoto MA, Batista AC, Lopes LC, de Góes FCGS, Consolaro A et al. Comparative study of tissue response to polyglecaprone 25, polyglactin 910 and polytetrafluorethylene suture materials in rats. Braz Dent J 2002;13(2):86-91.
- Kim JS, Shin SI, Herr Y, Park JB, Kwon YH, Chung JH. Tissue reactions to suture materials in the oral mucosa of beagle dogs. J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41(4):185-91.
- Saito CTMH, Bernabé PFE, Okamoto R, Okamoto T. Reação do tecido conjuntivo subcutâneo de ratos aos fios de sutura poliglecaprone 25 e poliglactina 910. Salusvita 2006;25(2):131-42.
- Javed F, Al-Askar M, Almas K, Romanos GE, Al-Hezaimi K. Tissue reactions to various suture materials used in oral surgical interventions. ISRN Dentist 2012:2012:762095.
- Rached RSA, de Toledo BE, Okamoto T, Marcantonio Jr. E, Sampaio JE, Orrico SR et al. Reaction of the human gingival tissue to different suture materials used in periodontal surgery. Braz Dent J 1992;2(2):103-13.